Introduction
A prominent institution in the field of investment banking is Deutsche Bank- a German-based financial institution. Over the years, it has been a century and contributed to the determination of the investment banking career path through its changes and dynamism. By analyzing the case of Deutsche Bank, it is possible to gain practical knowledge about the difficulties and opportunities of the banking industry, as well as skills required in investment banking. This case study will play a vital role in the success factors of the companies operating in the sphere.
Deutsche Bank’s Evolution in Investment Banking
Deutsche Bank's evolution in investment banking is characterized by several shifts and expansions in response to global factors. The bank established itself mainly in Europe, and investment banking emerged as one of the strategic streams in the later part of the twentieth century.
-
1980s-1990s: Expanded into the U.S and global markets pervasively by purchasing Morgan Grenfell in 1989 and Bankers Trust in 1998.
-
Early 2000s: Sustained the process of building up the company's image and established itself as one of the leaders in fixed income, equities, and M&A segments.
-
Financial Crisis of 2008: Suffered significant losses, particularly in the investment banking business, necessitating a major restructuring and reassessment.
-
Post-2010 Era: Concentrating on risk minimization, cost control, and organizational transformation to address new regulatory challenges.
It was these shifted strategic changes that assisted Deutsche Bank in becoming a benchmark global investment banking firm as it underwent market and regulatory pressures.
Strategic Initiatives and Business Model
Deutsche Bank's strategic steps and business model have been closely related to its prospects in the investment banking business. At the beginning of its expansion strategy, the bank aimed to increase its market position through mergers and acquisitions to incorporate other firms from across the globe.
Critical Components of Deutsche Bank’s Business Model:
-
Global Markets: This unit is responsible for the trade and sales of services, and products across all asset classifications, including stocks, bonds, and commodities. It is essential for enhancing liquidity and offers detailed market data and information.
-
Corporate Finance: Operating as a specialized advisory services unit, it assists clients with mergers, acquisitions, and raising capital. This is especially important in setting up and performing many intricate economic transactions.
-
Asset Management: This division offers investment products and services to institutional and retail investors, with a main focus on portfolio management and investment planning.
The bank’s recent strategic reorientation signifies its desire to improve its investment banking skills and goals, adjust to new conditions, and focus on key activities.
Case Analysis: Deutsche Bank’s Transformation Strategy
Investment banking giant Deutsche Bank had gone through tough times, including being plagued by fines, compliance concerns, and eroding profitability. This led to the firm initiating a concerted rebuild plan. This strategy was complex and included targeting structural problems as well as the perception of the market.
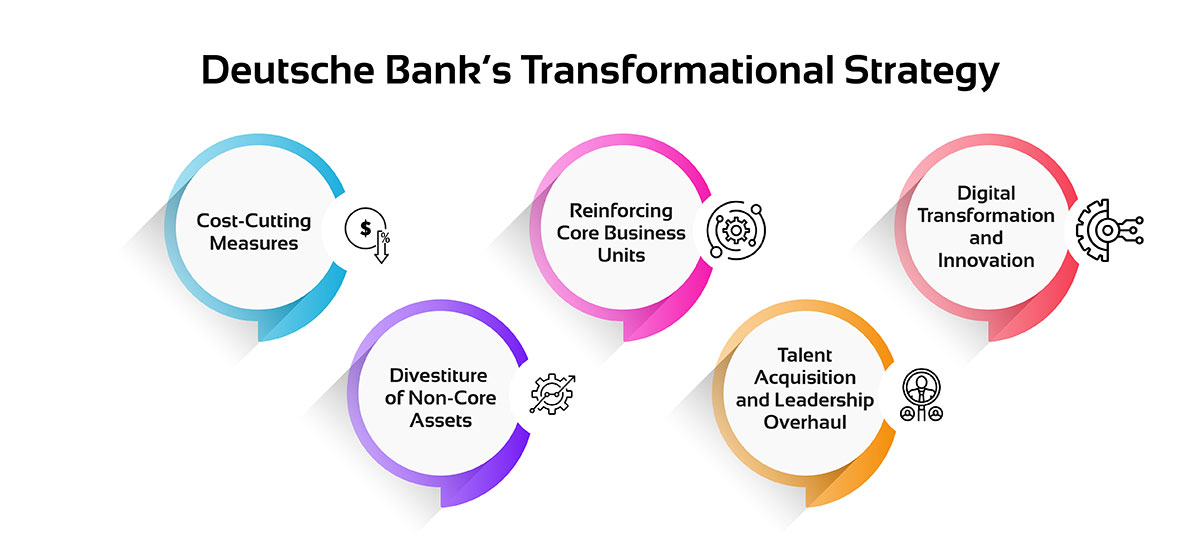
Key elements of Deutsche Bank's turnaround strategy include:
-
Cost-Cutting Measures: Operational expense reduction was one of the main levers, and the bank embarked on a severe cost-cutting exercise. This included reducing operational costs such as efficiency improvement, selling non-profit branches, and cutting headcount worldwide.
-
Divestiture of Non-Core Assets: To streamline investment banking, Deutsche Bank eliminated several non-strategic businesses and left non-crucial geographies. This helped the bank streamline its strategies and concentrate on areas that were the bank's key strengths, like Global Markets and Corporate Finance.
-
Reinforcing Core Business Units: Deutsche Bank reorganized its divisions into four areas of focus: Corporate Bank, Investment Bank, Private Bank, and Asset Management. This facilitated the carving out of efforts, focus, and resources in directions that were consistent with its long-term strategic direction in investment banking.
-
Talent Acquisition and Leadership Overhaul: The bank's management was aware of the skills required in investment banking and leadership in formulating the change. To achieve this, it recruited some of the best talents in the industry and changed the leadership in its investment banking arm.
-
Digital Transformation and Innovation: Deutsche Bank made special efforts in the digital drive, which included enhancing technology to streamline operations and improve client satisfaction. This was meant to help the bank strengthen its investment banking and start branding itself as a digital bank.
This strategic plan, together with the goals mentioned above, can be said to demonstrate Deutsche Bank's strategic move to strive and rebuild market confidence and efficiency to be among the best investment banking firms in the market.
Lessons Learned: Investment Banking Skills and Strategies from Deutsche Bank
The experience of Deutsche Bank in investment banking can provide valuable lessons about the competencies and processes required to excel in the field. Any professional eyeing an investment banking career must explore how the bank tackles challenges, risks, and market dynamics to define the right trajectory for the job. Key lessons include:
-
Adaptability to Market Dynamics: This shows Deutsche Bank's flexibility. The bank changes its strategies to fit the new market conditions. These changes increase the demands on investment bankers, who need to develop versatility and adaptability to shift their strategies.
-
Risk Management Expertise: The bank's suffering regulatory penalties sufficiently illustrate the importance of risk management skills. Risk managers need to learn about economic and non-economic risk factors to avoid adverse situations.
-
Focus on Core Competencies: By selling off these non-core assets, Deutsche Bank improved on the key success factor of concentrating on core competencies. Anyone who wants to be a banker should now define areas of specialization and ensure they develop them to enhance their sustainability.
-
Client Relationship Management: Therefore, Client relations must be developed and maintained well. Analyzing Deutsche Bank’s initiatives, the paper establishes that trust and long-term relationships propel development in investment banking.
Comparative Analysis: Deutsche Bank vs. Other Major Investment Banks
Deutsche Bank’s experience in investment banking involves successes and failures that distinguish it from other global banks. This section also compares Deutsche Bank to other important investment banks in terms of its performance, strategy, and the market it occupies.
-
Revenue Comparison: Deutsche Bank's revenue from investment banking has risen and fallen because of shifting strategies and marketing influences. Compared to industry titans such as Goldman Sachs or JPMorgan Chase, restructuring is promising for Deutsche Bank's future development.
-
Market Share: Deutsche Bank has suffered its market share shrinking in the last few years, but targeted operations in the European markets are expected to boost the shrinking market share. On the other hand, the competitors have strengthened themselves through diversification and technology.
-
Strategic Focus: Unlike some competitor banks that have strategically embraced technology, Deutsche Bank has focused on other core banking competencies. However, recent trends have shown a shift to a more strategic approach, which is digital transformation.
Conclusion
This analysis of Deutsche Bank’s experience in investment banking demonstrates an intricate and lengthy process of sustaining a competitive market position. The market strategies, restructuring measures, and emphasis on the essential competencies shape valuable lessons on managing volatilities and uncertainties at the bank. They can analyze and discuss successes and failures that can be used to create robust investment banking career path in the face of shifting industry forces and future trends.

