Introduction
Financial modeling is a fundamental tool in finance, emerging with the complexity of investment banking, corporate finance, and decision-making. Financial modeling with Excel enables professionals to analyze data, predict results, and determine an organization's financial health seamlessly. As Excel continues to be the universally adopted tool for modeling complex financial models, mastering this competency augments analytic skills and wields investment banking proficiency; hence, it remains pertinent for career progression in finance.
Core Concepts Behind Financial Modeling
Financial modeling refers to the task of constructing a model that represents a firm’s financial information to support analysis, planning, and decision-making. It assists working people in assessing firms, securities, and initiatives based on distinct presumptions relating to profits.
Main components of financial models include:
-
Assumptions: Variables include growth rates, interest rates, and the organization's cost estimations.
-
Inputs: Financial information that is publicly available and historical financial data.
-
Calculations: Financial ratios and quantitative models that predict future outcomes.
-
Outputs: The final analysis includes a valuation, cash flow, or any other profitability model.
Financial modeling is vital in areas such as valuation, capital budgeting, and investment analysis. Therefore, professionals in the finance sector, especially investment banking, need to know how these two ideas work in harmony to produce precise insights.
Types of Financial Modeling: From Simple to Advanced
Financial modeling is an essential tool in many fields, including investment banking and management during the business. Every model is unique in its application. Thus, a person should grasp multiple types of financial modeling. Below are some of the most common types, ranging from simple to advanced:
-
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Model: The DCF model is among the most popular models for assessing the value of a company or an asset based on projected cash flows and their present value. It is a must-know tool in investment banking and valuation appraisal.
-
Merger and acquisition (M&A) Model: This model is useful in determining the fiscal effectiveness of mergers and acquisitions for potential synergies and cost-effective avenues in a deal. It generally involves amalgamating two firms’ financial statements to analyze their results after a merger.
-
Leveraged Buyout (LBO) Model: The LBO model used in LBOs and private equity firms to determine the viability of consolidation of a firm based on debt. Returns to equity investors are computed in this model while evaluating the capability of the target firm to sustain the debt.
-
Budgeting and Forecasting Models: These models assist organizations in forecasting their revenues, expenses, and cash flows during the following periods. They are normally implemented in corporate finance to coordinate resources with expected objectives.
All these types of financial modeling provide different perspectives, and the proficiency of multiple models inculcates cross-expertise in investment banking. These models range from the simple DCF model to the elaborate LBO and, as we have seen, they play a central role in the decision-making process.
Why Excel is the Industry Standard for Financial Modeling
Microsoft Excel continues to dominate financial modeling due to its flexibility, ease of use, and use in computationally intensive tasks. Whether constructing a basic cash flow model or an advanced leveraged buyout (LBO) model, Excel can facilitate the organizing, analyzing, and reporting of financial data in a systematic and uncluttered platform.
Key reasons why financial modeling in Excel is so widely adopted include:
-
Flexibility: Excel is flexible in such layouts, inputs, and formulas that can be substituted/replaced according to the specifications of the financial model in question.
-
Functions and Formulas: Financial analysis is conducted easily with special functions such as VLOOKUP, SUMIFS FUNCTIONS, and INDEX MATCH FUNCTIONS.
-
Data Visualization: Excel has highly effective built-in charting features, and PivotTables reconstructs received data into simple charted information.
-
Accessibility: Excel is currently standard software in most organizations worldwide. It has many functionalities, especially in collaboration and analysis of financial data.
Despite the availability of specific software, flexibility, ease of use, and versatility make Excel a popular tool for financial officers in businesses such as investment banking and corporate finance.
Step-by-Step Process for Building a Financial Model in Excel
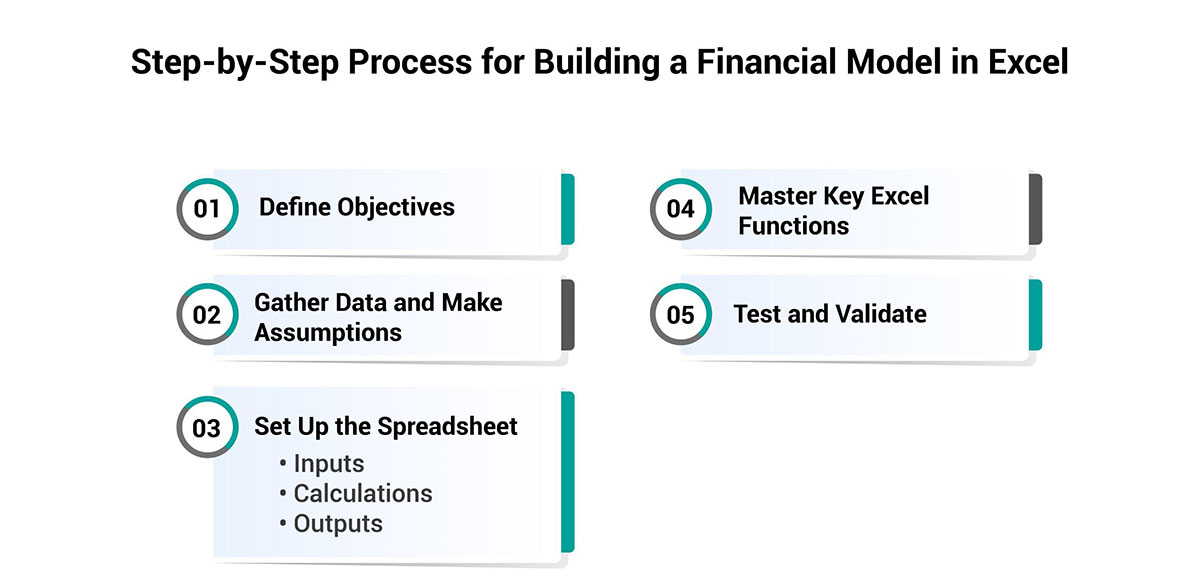
When creating a financial model in Excel, note that specific guidelines must be precise, understandable, and easy to use. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you craft a robust model:
-
Define Objectives
When developing the model, make sure to state the reason for creating it. Is the model you are developing a cash flow forecast, a valuation model, or a budgeting tool? Identifying the objective makes it easy to define your assumptions and the structural framework you will follow.
-
Gather Data and Make Assumptions
Acquire pertinent financial information, including historical financial statements, market trends, and economic indicators. Make clear what assumptions, such as growth rates, cost of capital, or margin, your model depends on.
-
Set Up the Spreadsheet
Organize your model into three main sections:
-
Inputs: For easier replacement during changes to model assumptions, put all the assumptions and inputs in one textbox area.
-
Calculations: Do all possible computations in an adjacent part of the layout and connect them to the inputs.
-
Outputs: The best way to integrate the conclusions section is to create a neatly separated space for financial forecasts or essential results such as cash flows, profit margins, or value ratios.
-
Master Key Excel Functions
Use Excel functions like:
-
VLOOKUP/INDEX MATCH is used to look up data.
-
VLOOKUPs for vertical lookups.
-
IF statements serve as the tool that helps control the scenario analysis process.
-
PivotTables where large amounts of data are presented and analyzed.
-
Test and Validate
Running sensitivity analyses on the model helps check for errors by comparing the results of the established model against various base cases. Check by comparing your findings with how you have previously done or how others in the same industry are doing it.
By following this structured approach, you will be able to create a robust financial model that is also very helpful.
Enhancing Your Financial Models with Advanced Excel Techniques
To advance your financial modeling knowledge in Excel, you must focus on the vital techniques that enhance the effectiveness of your models. Essential Excel functions help analyze data but are basic in functionality, while complex functions help a lot, particularly in financial organizations.
The most useful framework is scenario analysis, which enables the assessment of different outcomes depending on certain assumptions. Goal Seek and Solver of Excel are also important when it comes to generating financial models since they provide a method to determine the input level that will generate specific output.
Additionally, the use of Macros and VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) automates processes, thus reducing the time taken in repetitive processes and providing uniformity in models.
Here are three critical advanced techniques to implement:
-
Scenario Analysis: Analyze different financial results depending on the changes in certain assumptions.
-
Goal Seeker and Solver: Use math to optimize the company’s performance in order to reach a certain financial performance level.
-
Macros and VBA: To increase effectiveness and eliminate errors in financial modeling.
Implementing these techniques will improve your models' accuracy and the results' usability threefold.
Conclusion
Financial modeling in Excel is crucial for any aspirant planning to thrive in investment banking skills. Acknowledge types of financial modeling and enhance your technical skills in Excel functions, making you more viable in the business world. Training is also essential in the growth of a given career since it sharpens skills and updates the individual with market trends. Learn and apply the skills needed to face the complicated environment in the field of finance and to succeed in it.

