
From the ever-changing universe of investment strategies and valuation methods, the Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) analysis is another star leaving a financial trail that that will help you analyze the value of an investment. However, DCF analysis is not a tool, it is the approach which is employed by the analysts, investors, and managers using the technique to value the security.
This guide is designed to demystify DCF modelling, by explaining the overall process and its usage in different situations, as well as the two main types of DCF models. Whether you are a wealth manager, a rookie investor, or a finance student, it is paramount that you are well-versed in DCF analysis to excel in finance career which is quite complex now. So, here we deal with DCF in detail considering the mechanism and then illustrate its application in the area of financial decision-making.
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) is a common and very popular capital budgeting methodology that determines the value of the investment based on discounted cash outflows and inflows. It has used the notion that actual money today has a higher value than money of the same amount in the future due to its earning capability and the assumed possibility that interest rates cannot be always guaranteed. DCF analysis brings an investor into calculating or considering the time value of an investment as an opportunity or the attractiveness of the investment.
The three primary components of the DCF are:
Future Cash Flows: The first thing in calculating DCF position is to assume the future cash flows which can be generated from the investment. Most of these cash flows would be of the nature of the revenue, operating expenses, and taxes, while the others will be categorized as capital expenditures. Estimate the returns of the investment based on the sector, value chain and dynamics of the market as well as the factors that might influence the business.
Discount Rate: The next most important aspect is the discount rate which is also referred to as the required rate of return or cost of capital. The rate denotes a chance of loss of the money invested with the individual and the risk level is represented in this rate. It refers to the money that is being spent, and it has a present value.
Present Value: For this, DCF analysis applies the discount rate in which all future cash benefits are turned into today’s worth. Like that, it provides an estimation of the intrinsic value of the investment. The present value of the entire stream of forecasted money flows represented by the investment is the total value.
Discounted cash flow (DCF) computation requires a few basic steps which need to be observed to derive the right valuation of an investment. Here is a detailed guide:
Forecast Future Cash Flows: First, determine the net future cash flows that the investment will bring if you buy it. These money flows are to be prognosticated to a particular term of subscription, usually a span from five to ten years, in fact, according to the nature of such investment. It is equally important to have assumptions for the revenue growth, expenses and other such factors that are vital for the business plan.
Determine the Discount Rate: Of main importance in DCF analysis is the loan rate, or a required rate of return as well as the cost of capital. It indicates the opposite result, which is not using this money to spend on projects or investments we are contemplating. The discount rate is subject to the riskiness of the investment and includes factors like the industry’s beta, the prevailing market conditions, or the industry’s risk level.
Calculate the Present Value of Future Cash Flows: The required discounting into its current value by the chosen rate is employed for all future cash flows. The formula for calculating the present value of a cash flow is:
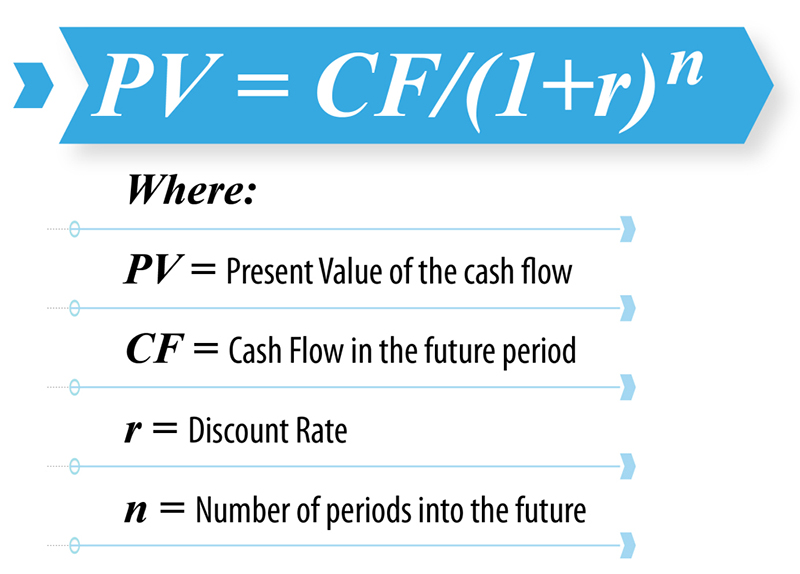
Sum the Present Values: Consider the future cash flow present value by calculating these values then sum them up to figure out the total present value of your investment. Through this number, the investor hopes to estimate the vehicle’s operation based on the forecasted cash flows and the selected discount rate.
Consider Terminal Value: Terminal values of an investment may be required depending on the situation where a business wants to stipulate the value of an investment at the end of the given time frame. This can be treated diversely using several techniques which include the Gordon Growth Model and the Exit Multiple Method, and is added to the present value of future cash flow and is used to compute the value of an investment.
Calculate Net Present Value (NPV): Finally, determine the Net Present Value by deducting the initial investment or cost from the total present value summed up from the streams of future cash-flows. By definition, a positive NPV is the indication that the investment is to generate returns greater than the required rate of return. This is, subsequently, what makes the investment highly attractive.
DCF analysis, demands a multipurpose consideration in the realm of finance, catering as the key to prosperous investment strategies as well as representing a core valuation method. Therefore, the main factor of investing is diversification—evaluating the attractiveness of investment projects, and it allows investors to make quantitative-based decisions. Using the DCF method, investors can find investment assets whose series price relationship to market factors might indicate that they are undervalued or overvalued.
In addition, through the DCF analysis, corporate finance gets a tool for capital budgeting activities whereby project viability or acquisition is assessed. The result is that a company makes the right choice. It also empowers strategic planning by assisting in understanding the money implications in the short and long-term of various projects. Therefore, DCF is also used for calculations of the fair value of a company’s stock, and it is seen as an effective tool for asset valuation for investors or analysts who are responsible for determining the investment potential of a publicly traded firm.
DCF technique applies various approaches, adapted to the specific valuation methods of every scenario.
Discounted Dividend Model: The dividend discount model is a technique for valuing stocks that assumes that stock prices vary based on the expected future dividends. It is predicated on the condition that dividends are the only type of cash flow investors would get.
Discounted Free Cash Flow Model: The DCF approach measures the monetary inflows available for all the providers of capital, including the shareholders and the creditors. Through a process which calculates the present value by discounting the free cash flows, the analysts will eventually establish the overall value of the company or project.
Adjusted Present Value Method: The imputation method is based on the debt tax effect recognition. It sets the present value of the project’s cash flows to the extent that they are tax-shielded by debt leverage.
Economic Value-Added Model: This approach focuses on the value created by operations. It deducts capital cost from the net operating profit after tax and henceforth, aids in determining the value addition of the company.
The use of DCF models includes industries and sectors of different kinds. Financial analysts, investment bankers, corporate finance experts, and equity researchers commonly employ DCF analysis in their decision-making processes. Moreover, business people such as owners and entrepreneurs also employ DCF to establish the worth of their business and make crucial strategic decisions.
In addition, DCF analysis is the keystone of financial and investment theory at the university level and is taught in central finance and investment courses. Its spread use substantiates its efficiency in assessing investment opportunities and providing guidance on financial planning crucial for anyone who bears any financial relation.
In conclusion, a DCF is an indispensable instrument in the portfolio of valuation methods and investment strategies. Through the conversion of future cash flows to their present value using the DCF technique, an investor gains a structured process estimating an asset value.
Whether you are a skilled investor, a corporate manager, or an aspirant in finance you should grasp DCF analysis, which is an important tool for informed financial decisions as well as the complexities of the investment world. Thus, jump into the depths of the DCF with the aid of the wisdom of the right decision-making and the ability to recognise value and capitalise on financial opportunities.